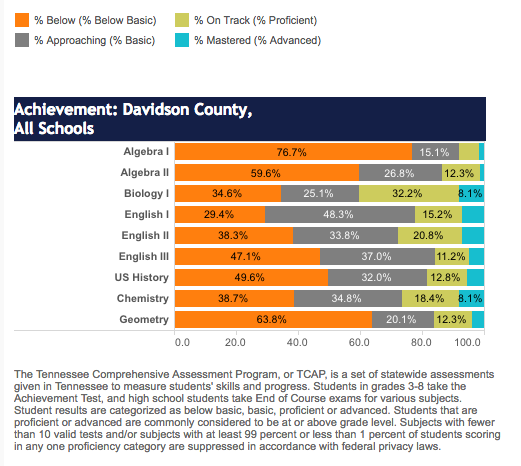
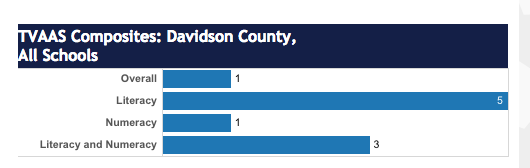
Members of the Murfreesboro City School Board are not happy with the slow pace of results coming from the state’s new TNReady test. All seven elected board members sent a letter to Commissioner of Education Candice McQueen expressing their concerns.
The Daily News Journal reports:
“However, currently those test scores seep ever-so-slowly back to their source of origin from September until January,” the letter states. “And every year, precious time is lost. We encourage you to do everything possible to get test results — all the test results — to schools in a timely manner.
“We also encourage you to try to schedule distribution of those results at one time so that months are not consumed in interpreting, explaining and responding to those results,” the letter continued.
A Department of Education spokesperson suggested the state wants the results back sooner, too:
“We know educators, families and community members want these results so they can make key decisions and improve, and we want them to be in their hands as soon as possible,” Gast said.. “We, at the department, also desire these results sooner.”
Of course, this is the same department that continues to have trouble releasing quick score data in time for schools to use it in student report cards. In fact, this marked the fourth consecutive year there’s been a problem with end of year data — either timely release of that data or clear calculation of the data.
TDOE spokesperson Sara Gast went further in distancing the department from blame, saying:
Local schools should go beyond TNReady tests in determining student placement and teacher evaluations, Gast said.
“All personnel decisions, including retaining, placing, and paying educators, are decisions that are made locally, and they are not required to be based on TNReady results,” Gast said. “We hope that local leaders use multiple sources of feedback in making those determinations, not just one source, but local officials have discretion on their processes for those decisions.”
Here’s the problem with that statement: This is THE test. It is the test that determines a school’s achievement and growth score. It is THE test used to calculate an (albeit invalid) TVAAS score for teachers. It is THE test used in student report cards (when the quick scores come back on time). This is THE test.
Teachers are being asked RIGHT NOW to make choices about the achievement measure they will be evaluated on for their 2017-18 TEAM evaluation. One choice: THE test. The TNReady test. But there aren’t results available to allow teachers and principals to make informed choices.
One possible solution to the concern expressed by the Murfreesboro School Board is to press the pause button. That is, get the testing right before using it for any type of accountability measure. Build some data in order to establish the validity of the growth scores. Administer the test, get the results back, and use the time to work out any challenges. Set a goal of 2019 to have full use of TNReady results.
Another solution is to move to a different set of assessments. Students in Tennessee spend a lot of time taking tests. Perhaps a set of assessments that was less time-consuming could allow for both more instructional time and more useful feedback. I’ve heard some educators suggest the ACT suite of assessments could be adapted in a way that’s relevant to Tennessee classrooms.
It will be interesting to see if more school districts challenge the Department of Education on the current testing situation.
For more on education politics and policy in Tennessee, follow @TNEdReport