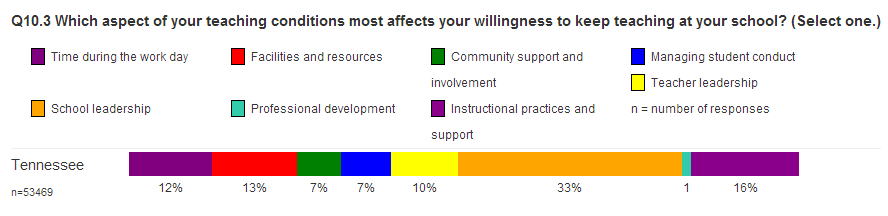
According to a recent report, Tennessee’s education policies have resulted in our state becoming a national leader in at least one category. The Learning Policy Institute notes that Tennessee has the highest percentage of 1st- and 2nd-year teachers of any state in the nation. Nearly 20% of Tennessee’s teacher workforce is very new to the profession. That’s well above the national average of 12.7%. When that number is combined with the percentage of uncertified teachers (4.1%), the outlook is not good: Our schools are not retaining experienced teachers. The national average for classrooms staffed by uncertified teachers is 2.6%.
Check out the data:
Teacher compensation in Tennessee is certainly one factor playing into this challenge. Our teachers are paid 27.3% less than individuals in similarly trained professions. In fact, we have among the highest teacher wage gaps in the country.
Helpfully, the Learning Policy Institute offers some recommendations for improving this situation:
Service scholarships and student loan forgiveness:
The cost of high-quality teacher preparation is a significant obstacle to those considering entering the teaching profession. To overcome such barriers, at least 40 states have established service scholarship and loan forgiveness programs to recruit and retain high-quality teachers. These programs underwrite the cost of teacher preparation in exchange for a number of years of service in the profession. Research has found that effective service scholarship and loan forgiveness programs leverage greater recruitment into professional fields and locations where individuals are needed, and support retention.
High-retention pathways into teaching:
Teacher turnover is higher for those who enter the profession without adequate preparation. However, teachers often choose alternative certification pathways that omit student teaching and some coursework because, without financial aid, they cannot afford to be without an income for the time it takes to undergo teacher training. High-retention pathways are developed to subsidize the cost of teacher preparation and provide high-quality training for incoming teachers. These pathways include teacher residencies and Grow Your Own programs that recruit and prepare community members to teach in local school districts
Mentoring and induction for new teachers:
Evidence suggests that strong mentoring and induction for novice teachers can be a valuable strategy to retain new teachers and improve their effectiveness. Well-mentored beginning teachers are twice as likely to stay in teaching as those who do not receive mentoring. However, the number of states supporting mentoring and induction programs decreased during the recent recession, and a 2016 review of state policies found that just 16 states provide dedicated funding to support teacher induction. Under ESSA, states can leverage federal Title II, Part A funds to support new teacher induction and mentoring. Indeed, a number of states, including Delaware and Ohio, are taking such an approach. Other states have invested state funds to support new teacher induction, including Connecticut and Iowa.
High-quality school principals:
Principals play a central role in attracting and retaining talented teachers. Teachers cite principal support as one of the most important factors in their decision to stay in a school or in the profession. Therefore, states can benefit from building effective systems of preparation and professional development for school leaders. Title II, Part A of ESSA provides states with new opportunities to invest in and improve school leadership in ways that could increase teacher retention, including by reserving up to 3% of their state Title II, Part A funds for school leader development. Many states—including North Dakota and Tennessee—are seizing this opportunity, with nearly half of states using the optional 3% set aside and 21 states using ESSA funds to invest in principal preparation. The North Carolina Principal Fellows program is an example of a long-standing, successful state effort to support principal development.
Competitive compensation:
Not surprisingly, the lack of competitive compensation is one factor that frequently contributes to teacher shortages, affecting the quality and quantity of people planning to become teachers as well whether people decide to leave the teacher workforce. Even after adjusting for the shorter work year in teaching, beginning teachers nationally earn about 20% less than individuals with college degrees in other fields—a wage gap that widens to 30% by mid-career. Large inequities in teacher salaries among districts within the same labor market leave some high-need, under-resourced districts at a strong disadvantage in both hiring and retaining teachers. More competitive compensation can be a critical strategy to recruit and retain effective educators, although different approaches may be necessary depending on the state, regional, and district context.
Recruitment strategies to expand the pool of qualified educators:
In light of fiscal constraints, many states are also opting for low-cost policy solutions that expand the pool of qualified teachers. Such strategies include recruiting recently retired teachers back into the classroom to fill open positions and strengthening licensure reciprocity to ease undue burdens to cross-state mobility and allow experienced and accomplished educators the opportunity to seamlessly transition into service in a different state. Colorado, for example, is actively pursuing both strategies, and Idaho, Oklahoma, and West Virginia are also recruiting retired teachers to help address teacher shortages.
Tennessee should certainly move forward with a serious effort to improve teacher compensation as well as an early career mentoring/induction program. Coupling these two items with meaningful new investments in our schools could make both coming to and staying in teacher a more attractive proposition in our state.
Until then, it’s likely we’ll continue to see teachers leave the profession at higher than the national rate. We simply haven’t been committed to investing in our teachers and it shows.
For more on education politics and policy in Tennessee, follow @TNEdReport
Support TNEdReport and keep the education news flowing!