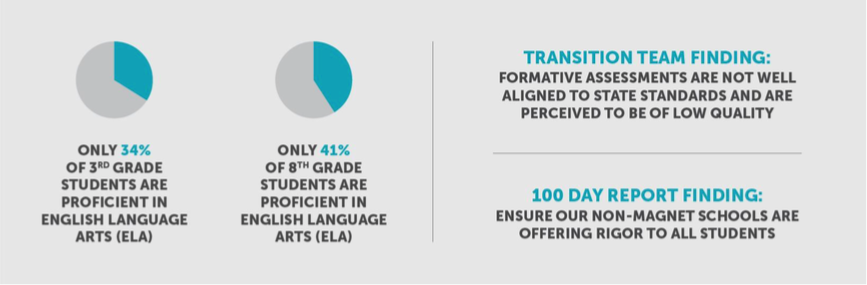
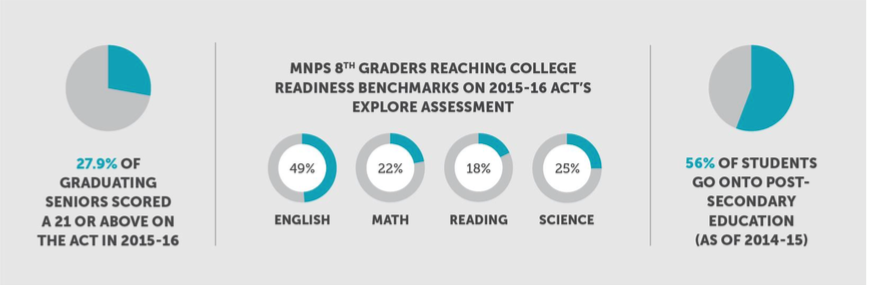
This week, Education Committees in the House and Senate will consider a number of bills creating school vouchers in Tennessee. Proponents are pushing the bills even as growing evidence suggests vouchers fail kids.
So, what would happen if Tennessee started a voucher program, even a small-scale one, this year?
One state with a record on this is Indiana. Vouchers started there back in 2011 in a relatively small program with fairly strict eligibility requirements. At the time the vouchers were created, then-Governor Mitch Daniels said:
Back in 2011, Daniels spoke to a conservative think tank a few months after he signed the program into law. At that speech, he said he didn’t expect this to become a big problem.
“It is not likely to be a very large phenomenon in Indiana,” he said “I think it will be exercised by a meaningful but not an enormous number of our students.”
Initially, vouchers were only to serve some 7500 students.
Fast forward five years, and the program has expanded exponentially, serving more than 30,000 students — 3 percent of the state’s student population.
The qualifications have changed, too. Now, a student doesn’t even have to have attended a public school to qualify for a voucher. Reports suggest this provision means Indiana is spending some $54 million supporting private schools — money that would not have been spent without the voucher program:
A report on the program released by the Department of Education shows the program costs $54 million.
“If the idea behind a voucher program is we’re going to have the money follow the student, if the student didn’t start in a public school, the money isn’t following them from a public school, it’s just appearing from another budget,” [Researcher Molly] Stewart said. “And we’re not exactly sure where that’s coming from.”
Vouchers, then, create $54 million in new expenditures — an education funding deficit — in Indiana.

To put that state’s program growth into perspective, 3 percent of Tennessee’s student population would be 29,936. The Tennessee voucher district would be the 8th largest district in the state, just larger than Sumner County and slightly smaller than Montgomery County. And, if our experience is at all like Indiana’s, about half of those students will never have attended a public school.
Nearly 15,000 students who never attended public school suddenly receiving vouchers would mean a state cost of $98 million. That’s $98 million in new money. Of course, those funds would either be new money (which is not currently contemplated) or would take from the state’s BEP allocations in the districts where the students receive the vouchers.
Let’s look at Davidson County as an example. If three percent of the student population there took vouchers, and half of those were students who had never attended a public school, the loss to the district would be a minimum of $8.4 million.
This means local governments would be stuck picking up the tab to support private schools. The alternative would be a dedicated state fund to support the voucher school district. That’s a total cost of around $200 million, half of that new money.
Should taxpayers be asked to invest $100 million in a program that gets negative results? Studies in Indiana, Ohio, and Louisiana all indicate that vouchers have a negative impact on student academic outcomes.
Kevin Carey noted recently that even a study by the Fordham Institute showed negative results for vouchers:
In June, a third voucher study was released by the Thomas B. Fordham Institute, a conservative think tank and proponent of school choice. The study, which was financed by the pro-voucher Walton Family Foundation, focused on a large voucher program in Ohio. “Students who use vouchers to attend private schools have fared worse academically compared to their closely matched peers attending public schools,” the researchers found. Once again, results were worse in math.
This week, we may hear that any new voucher program will start small and will only serve a fraction of our state’s students. Even if that’s true, the cost to taxpayers at the state and local level will be significant. Then, there’s the fact that studies are emerging showing vouchers just don’t work. Why spend more to get less?
For more on education politics and policy in Tennessee, follow @TNEdReport